One week hypofractionated breast radiotherapy acute toxicity with SIB and regional nodal irradiation
Guillermo Potdevin-Stein,
Spain
PD-0230
Abstract
One week hypofractionated breast radiotherapy acute toxicity with SIB and regional nodal irradiation
Authors: Guillermo Potdevin-Stein1, Aragón Cristian C.2, Alexandra Vallejo2, Iván Libreros2, Isabella Storino2, Carolina Echeverri2, Diego E. Santa-María2, Gabriel A. Marín2, Carlos A. Buelvas2, Raquel Ciérvide3, Ángel Montero-Luis3
1Hospital Universitario de Gran Canaria Dr Negrín, Radiation Oncology, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain; 2Hospital Universitario Fundación Valle del Lili, Radiation Oncology, Cali, Colombia; 3Hospital Universitario HM Hospitales, Radiation Oncology, Madrid, Spain
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
One-week-hypofractionated-radiation treatment (OWHRT) is not inferior to the 3-week-hypofractionated-regimen in disease control and acute toxicity (AC). The objective is to describe our experience using this ultra-hypofractionated schedule for whole breast/chest wall (WB/CWI) and regional nodal irradiation (RNI), internal mammary chian (IMC) and a simultaneous integrated boost (SIB).
Material and Methods
We conducted a prospective register of postoperative OWHRT for breast cancer patients. All patients were treated with either conformal or IMRT/VMAT and image guide radiotherapy (IGRT) with a dose of 26Gy/5.2Gy to whole breast/thoracic wall, and if indicated, lymph node areas, and a SIB of 29Gy/5,8Gy for tumor bed. Tolerance was evaluated at 1 month and 3 months after finishing OWHRT and every 6 months thereafter and graded according to RTOG/EORT and LENT/SOMA criteria.
Results
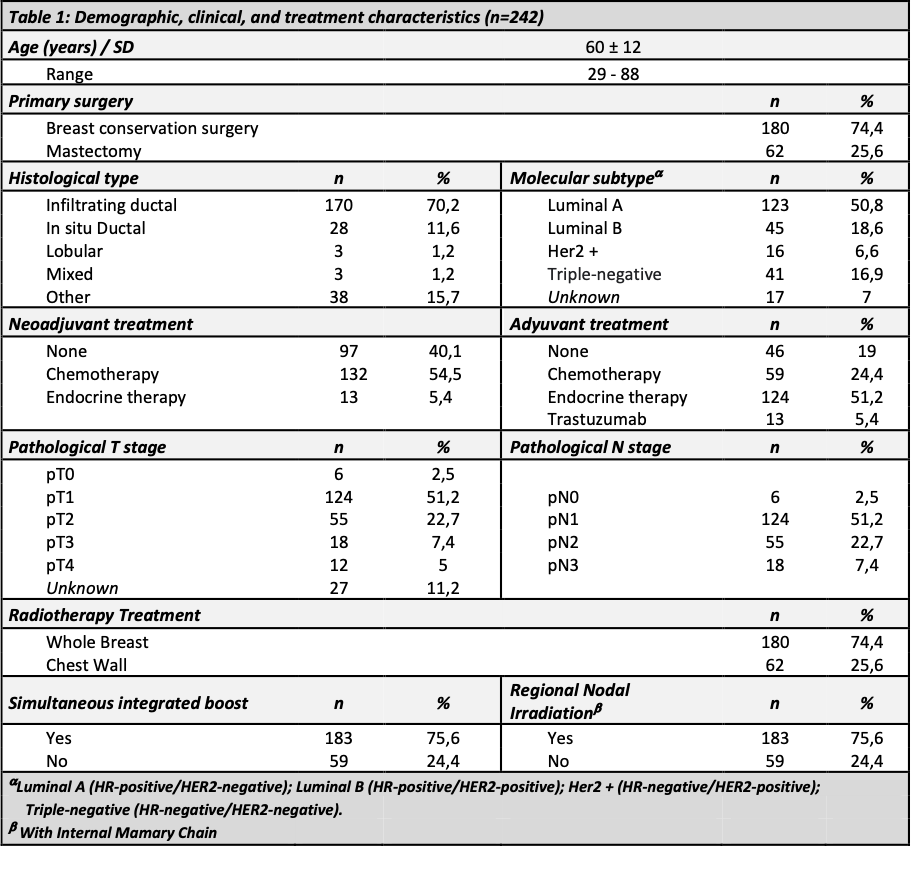
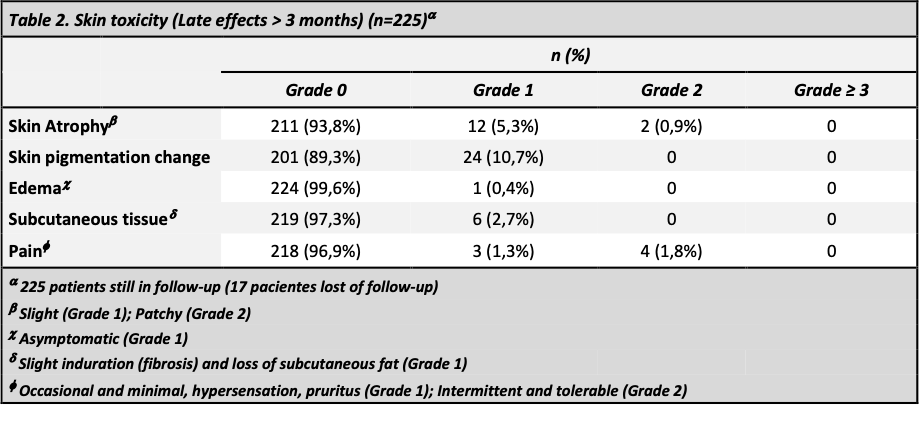
From may 2020 to April 2021, 242 female patients with a median age of 60±12 were included. Complete characteristics of enrolled patients are detailed in Table 1. A total of 183p (76%) were treated with SIB and 123p (51%) underwent RNI and IMC. With a median follow-up of 20 months (16-23 months), acute skin toxicity at one month was: grade 1 in 113p (47%) and grade 2 in 64p (27%) with no cases of ≥grade 3 toxicity. In the group of patients undergoing RNI , 36p (15%) reported grade 1 and 2p (0,8%) grade 2 esophagitis. No relationship was found between RNI with higher acute-skin-toxicity (Chi square p=0.001). None of the patients presented acute pulmonary or cardiac toxicity. At more than three months 225 patients continue follow-up (late effects). Skin-toxicity occurred in 37p (16,44%) grade 1 and 2p (0,9%) grade 2, pain 3p (1,3%) grade 1 and 4p (1,8%) grade 2 (Table 2), and none presented esophageal, pulmonary or cardiac toxicity.
Conclusion
This initial results shows that OWHRT with SIB for WB/CWI and RNI with IMC seems to be feasible and well tolerated. Future studies with larger number of patients and longer follow-up are needed to confirm this results.