Bladder wall dose in PCa patients treated with stereotactic, daily adaptive MR-guided radiotherapy
Eline de Groot - van Breugel,
The Netherlands
PO-2347
Abstract
Bladder wall dose in PCa patients treated with stereotactic, daily adaptive MR-guided radiotherapy
Authors: Eline de Groot - van Breugel1, J.C.J. de Boer1, T. Willigenburg1, J. Hes1, J.R.N. van der Voort van Zyp1
1UMC Utrecht, Radiation Oncology, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Recently, we have clinically applied a sub-fractionation workflow for intrafraction re-planning during prostate SBRT on a 1.5 Tesla MR-linac (Unity, Elekta AB) in over 80 patients. This workflow counters intrafraction prostate motion and 2-3 mm planning margins were applied. Before sub-fractionation, we applied more generous planning margins. We investigated if the current sub-fractionation workflow results in a relevant decrease in bladder wall dose.
Material and Methods
Since 2019, we have been treating prostate cancer patients with 5 x 7.25 Gy on our MR-linacs, using daily imaging, re-contouring and re-planning (‘adapt to shape’ workflow). In 130 of these patients, Willigenburg et al (Rad Onc 2022, 171:182-8) reconstructed delivered dose to the bladder and bladder wall and investigated the relation with acute patient reported urinary toxicity. They found that absolute bladder wall dose was most predictive for treatment related toxicity, i.e. V25Gy > 9cc. We therefore compared the dose to the bladder wall for the sub-fractionation workflow with CTV-PTV margins of 2, 2 and 3 mm for LR, SI and AP directions of 25 IMRT pre-treatment plans with the dose in the bladder wall of 25 IMRT pre-treatment plans with an isotropic CTV-PTV margin of 5 mm. To solely focus on the impact of margin reduction, the V25Gy constraint was not yet applied in these plans. The bladder was defined as the entire volume circumscribed by the outer bladder wall, including the bladder content. For practical reasons, the bladder wall was created by 4 mm contraction of the outer bladder wall (Figure 1), following the experience from Willigenburg et al (2022) and Maggio et al (PMB 2013, 58:N115).
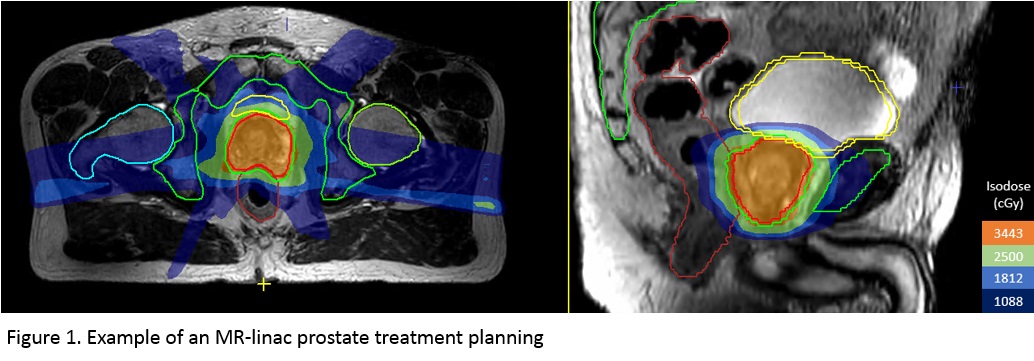
Results
The average V25Gy dose in the bladder wall for the 5 mm margin plans was 8.0±2.3cc (range 4-12.6cc) whereas for the 2-3 mm plans this was 5.9±1.5cc (range 4.2-9.7cc). This was a statistically significant difference (p < 0.01). The corresponding numbers of patients for which the V25Gy < 9cc constraint was violated were 7 (28%) and 2 (8%) respectively.
Conclusion
The clinically relevant bladder wall V25Gy was significantly higher in the 5 mm margin group than in the 2-3 mm group, even when this constraint was not explicitly applied during treatment planning. We therefore expect a lower GU acute toxicity rate in the sub-fractionation group and will present early results of patient reported toxicity in this group.