Dosimetric verification of small field SBRT plans using a new enhanced leaf model for VarianTruebeam
Michel Oellers,
The Netherlands
PO-1826
Abstract
Dosimetric verification of small field SBRT plans using a new enhanced leaf model for VarianTruebeam
Authors: Michel Oellers1, Ans Swinnen1, Frank Verhaegen1
1MAASTRO, Medical Physics, MAASTRICHT, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Supported by better diagnostic imaging, there is an increasing trend in radiation oncology to treat smaller tumors with a high dose in few fractions. Nevertheless hypofractionation in lung cancer remains challenging especially for very small targets with diameters below 1 cm. Current advanced dose algorithms like Acuros XB still have its limitations in predicting dose within 5% for small fields where for example inaccuracies in the MLC model may be amplified in the final dose prediction [1]. A way to improve the dose accuracy is by improving the current MLC model and more specific the way the leaf tips are modelled in Eclipse. A more realistic modelling of the leaf tips will most probably lead to a more accurate prediction of dose in very small targets.
Material and Methods
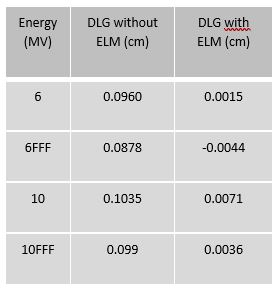
A pre-release of Acuros XB (version 18) with the new enhanced model (ELM) was used to determine new dosimetric leaf gap (DLG) values in Eclipse for Truebeam STx (Table 1). With these values the plans described in [1] were recalculated in Acuros XB pre-release version 18. Dose verification of the results were performed by EBT-XD film measurements in a dedicated CIRS dynamic thorax phantom and compared to the original results, based on Acuros XB version 15.6 [1].
Results
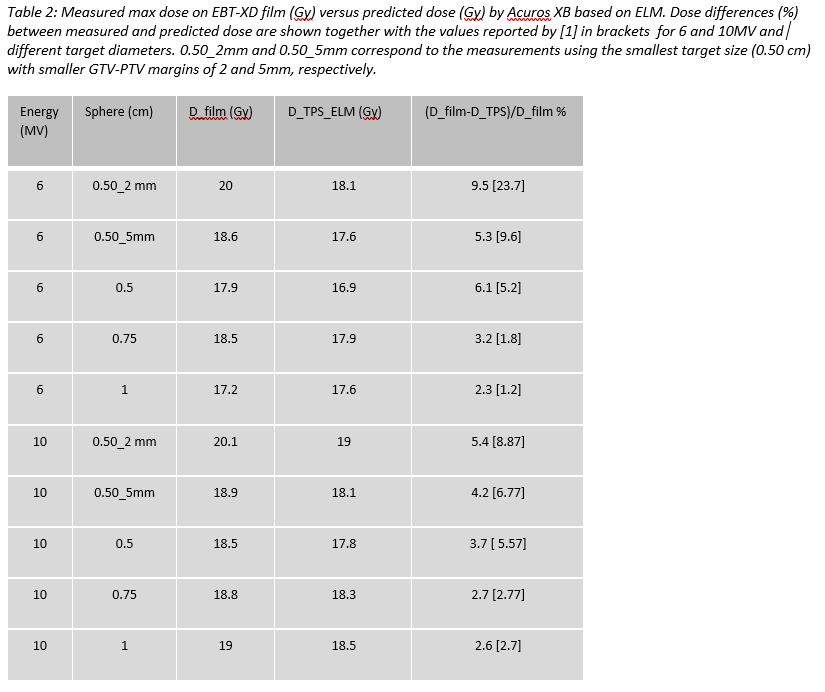
An improvement in dose prediction with the pre-released version 18 of Acuros XB, was seen compared to film measurements as shown in Table 2. Even for very small targets with diameters of 0.5cm a dose prediction accuracy around 5% or lower could be achieved, except for the smallest target s for 6MV.
Conclusion
The new ELM model significantly improves the predicted dose for very small targets going from 23.7% to 9.5% and from 8.9% to 5.4% for the smallest targets for 6 and 10 MV, respectively, compared to results shown in previous work [1]. On average the ELM model is able to achieve dose accuracies of around 5% for both 6 and 10 MV.
[1] Öllers MC, Swinnen ACC, Verhaegen F. Acuros® dose verification of ultrasmall lung lesions with EBT-XD film in a homogeneous and heterogeneous anthropomorphic phantom setup. Med Phys. 2020 Nov;47(11):5829-5837. doi: 10.1002/mp.14485