MRI-Linac patient QA: evaluation of single beam and region of interest specific gamma analysis
PO-1771
Abstract
MRI-Linac patient QA: evaluation of single beam and region of interest specific gamma analysis
Authors: Cintia de Almeida Ribeiro1, Matteo Galetto1, Matteo Nardini2, Gabriele Turco3, Lucrezia Bernabucci4, Nicola Franza5, Luca Indovina6, Lorenzo Placidi6
1Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Facoltà di Medicina e Chirurgia, Roma, Italy; 2Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCSS, UOSD Fisica Medica, Roma, Italy; 3Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCSS, UOC Radioterapia Oncologica, Roma, Italy; 4Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCSS, UOC Radioterapia Oncologica, Rome, Italy; 5Dosimetrica, Company, Nocera Inferiore, Italy; 6Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCSS, UOSD Fisica Medica, Rome, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Patient‐specific quality assurance (QA) in advanced radiotherapy techniques such as IMRT is an essential process to ensures correct machine-sided delivery of the prescribed dose by checking the accuracy of dose calculation and treatment delivery.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the performance of the Delta4 Phantom+ MR (D4), Scandidos, to different clinical plans on a 0.35T MR-Linac system (ViewRay MRIDIAN), comparing the patient-specific QA with another MR‐compatible 3D detector ArcCHECK (AC), SunNuclear. Additionally, only for D4, gamma analysis has been also evaluated at level of each single beam and each region of interest (ROI), including the most relevant OARs and PTV. IMRT QA failure rates has been finally analyzed in terms of machine parameters.
Material and Methods
Pre-treatment patient specific QA were delivered on D4 and AC devices, for a total of 20 clinical plans. These plans were divided in two different group: large rectum lesions (LRL), with SIB dose distribution, and small stereotactic lesion (SSL). Gamma analysis (90% global gamma passing rate at 3%/2mm with a 10% dose threshold) has been performed, based on the institutional tolerance. The single beams and single ROI evaluation have been performed in 10 clinical plans,in which 5 LRL plan and 5 SSL plan. For each of these treatment plans, only the beams that don’t achieve the minimum criteria established in our institution, were analyzed. IMRT QA failure analysis has been performed considering parameters such as number of MUs, number of segments per beam, gantry angle dependence, MLC shape, region where the gamma index (GI) fault. The patient ROIs were overlaid with the D4 virtual phantom and the measurement points were thereby grouped to what structure they belong, in order to perform a clinically relevant internal gamma analysis of ROI.
Results
Gamma analysis of the twenty plans shows similar result using the two MR-specific devices. (Fig 1). For our dataset, the percentual average difference was found as 2.32%± 1.64 to LRL, 2.24%± 1.58 to SSR and high concordance by Bland- Altman test. Although all plans passed the institution's gamma passing rate criteria, 9% and 2% of beam showed failures rate respectively for the LRL and SSL group (fig 2). A low weak Pearson correlation (R< 0.06) between the GI and the number of segments for both groups have been found. In the LRL group, 94% of the fault beams, had MU smaller than 9, large irregular segments and low GI in the gradient region of the PTV boost. For SSL group, weak Pearson correlation for all parameters (R<0.03) was also found; fails occur with irregular small fields and often localized in the central region of the PTV.
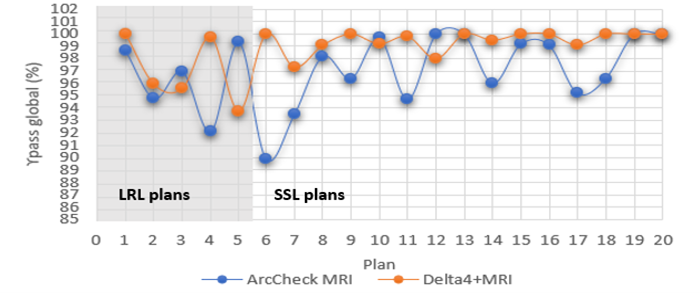
Fig1
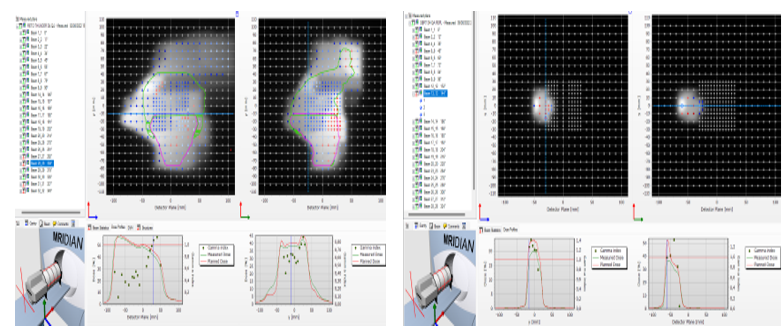
Fig2
Conclusion
Patient specific QA shows a high agreement between the D4 and AC devices, but the former showed higher gamma passing rate values. IMRT beam and ROI QA failure highlight a higher granularity analysis of the patient specific QA never investigate in the frame of MRI-Linac.