High-resolution CMOS detector array for robotic SRS treatment plan verification
PO-1766
Abstract
High-resolution CMOS detector array for robotic SRS treatment plan verification
Authors: Kim Holm1, Sinem Erdem1, Kai Schubert1, Jochen Krimmer2
1Heidelberg University Hospital, Department of Radiation Oncology, Heidelberg, Germany; 2IBA Dosimetry GmbH, -, Schwarzenbruck, Germany
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Robotic stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is able to deliver spatially precise, very small dose distributions. To verify these complex treatment plans, a 2D dose measurement with a sufficient resolution has to be performed. For this purpose, we have examined the usability of the IBA myQA SRS array which is based on a CMOS technology as it offers a resolution of 0.4 mm with no pixel spacing.
Material and Methods
X-ray dense markers (fiducials) were added to the myQA SRS array to be able to track its position with the Cyberknife (CK; Accuray Inc.) system. Different fiducial configurations were tested to achieve the lowest positioning uncertainty and highest flexibility for treatment plan verification.
The array characteristics such as a possible angular dependence and a dependence on the source-axis distance (SAD) were investigated and the possibility to correct for these effects was added to the evaluation software myQA (IBA).
Measurements of 12 typical patient treatment plans were carried out, a gamma index analysis with 1mm/3% criterion comparing the measured data with the data provided by the treatment planning system (TPS) were performed. The results were compared to the results from an ionization chamber (IC) array which has been used for treatment plan quality assurance (QA) in our clinic so far.
Results
Best positioning results were achieved with an additional plate added on top of the array containing eight fiducials and one fiducial below the array’s active area.
The myQA SRS array showed angular dependence resulting in deviations in the measured values of up to 20%; the SAD dependence was significantly lower (1-2%). Without any correction of these dependencies, the measured dose distributions deviated from the TPS data with results of 22-78% gamma pass rate. Applying the corrections in the myQA software, the results were significantly improved with more than 95% pass rate for nearly all treatment plans used. In contrast, pass rates of only 50-60% were achieved in some cases when using the IC array. These results are provided in detail in Table 1.
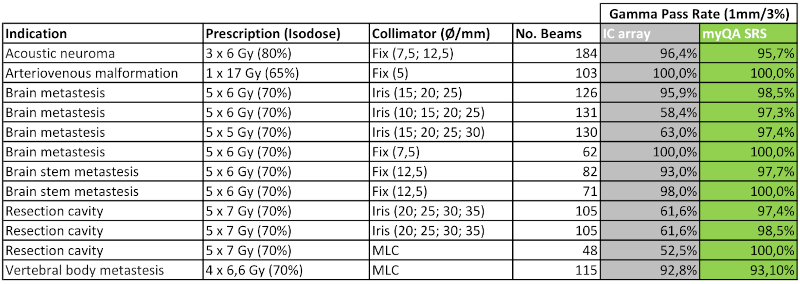
Table 1: Parameters of the patient treatment plans applied and gamma pass rates (1mm/3% criterion) of the comparison of the IC array used in routine today (grey) / the IBA myQA SRS array with angular and SAD correction applied (green) with the TPS data.
Conclusion
With angular and SAD corrections applied, the myQA SRS array provided very good results with significantly higher agreement with the TPS data than the IC array. With the fiducials added, it is therefore well suited for the verification of CK SRS plans.