The Clinical Effectiveness of SGRT on Extremities Patients: Accuracy and Potential Margins Reduction
PO-1836
Abstract
The Clinical Effectiveness of SGRT on Extremities Patients: Accuracy and Potential Margins Reduction
Authors: yanxin zhang1, Fukui Huan1, Xin Feng1, FengYu Lu1, ZhaoHui Li1, GuoYou Wei1, Wei Li1, HongJu Li1
1Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Radiation Oncology, Beijing, China
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Unlike other body sites, extremities patient positioning is challenging due to lack of comprehensive
immobilisation devices as well as familiarity of the staff experience. We would like to investigate if the
newly installed SGRT system could be clinically useful for extremities patients in terms of accuracy and
PTV margins reduction.
Material and Methods
24 random patients who were treated upper or lower extremities between September 2020 and
August 2021 were analysed retrospectively. 12 patients in the control group (Group A) used the
traditional setup method: lasers and skin markings (one anterior and two lateral). While the other 12
patients in the experimental group (Group B) used SGRT system (AlignRT, Vision RT) for patient setup.
In Group B, all patients were aligned within 1mm and 1° tolerance. A total of 209 and 168 CBCT images
were acquired for Group A and B respectively. Both translational and rotational shifts were recorded.
The positioning errors (Σ±σ): systematic errors (Σ) and random errors (σ) were calculated. Systematic
error was defined as the standard deviation of individual mean positioning error; random error was
defined as the root mean square of individual standard deviation positioning error. A formula of 2.5Σ
+0.7σ was applied for CTV to PTV margins calculation.
Results
The positioning errors for Group A and B were (2.52±3.08)mm and (1.14±1.43)mm, (2.26±2.51)mm
and (1.38±1.88)mm, (4.80±3.41)mm and (1.26±1.76)mm in x (lateral), y (longitudinal) and z(vertical)
directions; (0.82±1.12)° and (0.71±0.69)°, (0.52±1.18)° and (0.89±0.82)°, (1.49±1.14)° and (1.11±
1.53)° in Rx (Pitch), Ry (Roll) and Rz (Yaw) directions. The percentages of translational and rotational
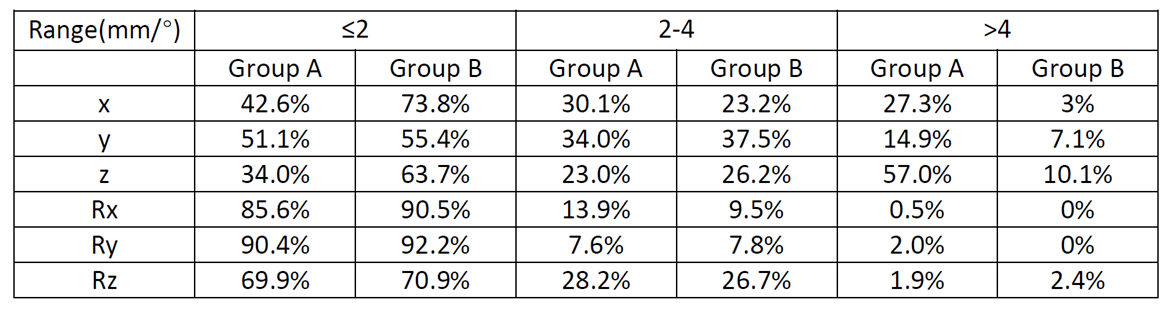
distribution errors were shown in the table 1. The calculated CTV-PTV margins were 8.5mm, 7.4mm,
14.4mm and 3.9mm, 4.8mm, 4.4mm in x, y and z directions for Group A and B respectively.
Table 1: The distribution errors of translational and rotational shifts.
Conclusion
The use of SGRT can improve the positioning accuracy especially in lateral and vertical direction.
Accurate and reproducible positioning could potentially reduce the PTV margins significantly for better
side effects management.