Hypofractionated salvage radiotherapy in patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer
PO-1422
Abstract
Hypofractionated salvage radiotherapy in patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer
Authors: Fabio Matrone1, Giuseppe Fanetti1, Alberto Revelant1, Jerry Polesel2, Paola Chiovati3, Giovanni Franchin1, Roberto Bortolus1
1Centro di Riferimento Oncologico di Aviano (CRO) IRCCS, Division of Radiation Oncology, Aviano, Italy; 2Centro di Riferimento Oncologico di Aviano (CRO) IRCCS, Unit of Cancer Epidemiology, Aviano, Italy; 3Centro di Riferimento Oncologico di Aviano (CRO) IRCCS, Division of Medical Physics, Aviano, Italy
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Hypofractionation
in salvage radiotherapy (SRT) for biochemical recurrence (BCR) of prostatic
cancer after prostatectomy is a debated
issue. We report the outcomes of 2 moderately hypofractionated schedules in pts
who received SRT to prostate bed for BCR.
Material and Methods
Pts
treated with Image
Guided-VMAT and a total dose of 65 Gy/26 fractions (Group A; BED=173.4 Gy for
α/β=1.5) or 66 Gy/30 (Group B; BED=162.8 Gy for α/β=1.5) were considered. Inclusion
criteria were: pN0/pNx, PSA at BCR ≥ 0.2 ng/ml and ≤ 1 ng/ml, no evidence of
pelvic/extrapelvic disease at restaging (when indicated), no pelvic irradiation
or boost on macroscopic local recurrence, follow-up ≥2 years and available
pre/post SRT data. Concomitant ADT was used prevalently in pts with high risk
features. Early and late toxicities were assessed using CTCAE Vers. 4.0.
Results
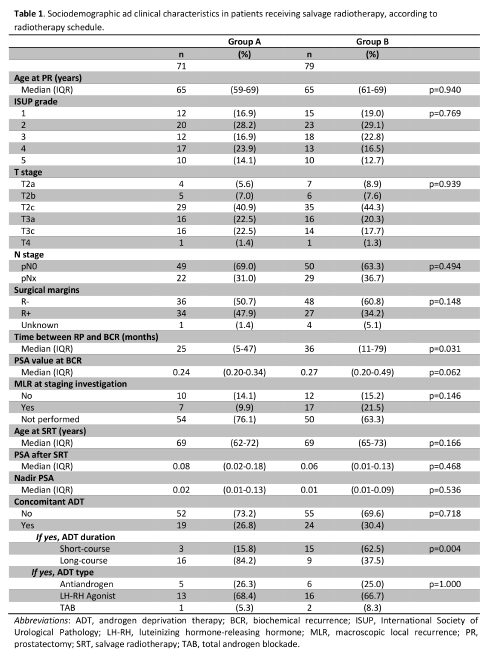
150 pts were
identified (Tab 1). Median follow-up was 67
months (IQR: 52-81) in group A and 38 (IQR: 30-46) in Group B (p<0.001).
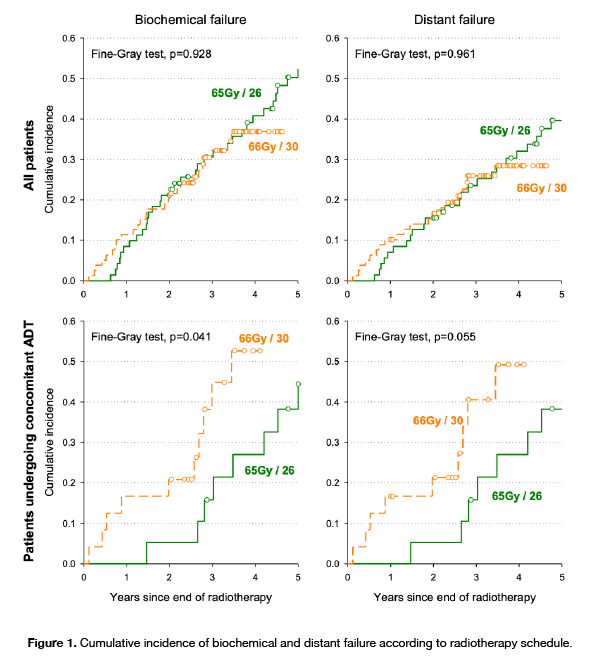
3-year recurrence rate of biochemical, local and distant failure in Group A and
Group B were 30.6% and 32.2% (p=0.928), 4.2%
and 6.1% (p=0.562), 23.5% and 25.9% (p=0.961), respectively (Fig 1). Among pts with
a distant failure pattern of relapse, 23 pts (82.1%) in Group A and 15 (71.4%)
in Group B had oligometastatic relapse (p=0.494); 5 pts (17.9%) in Group A and
6 (28.6%) in Group B had polimetastatic relapse. 5 pts in Group A (2 oligoprogressive
pts) and 4 pts in Group B (1 oligoprogressive pt) developed mCRPC; median
hormone-sensitive time was 57 months in Group A and 14 in Group B. 3-year OS was 100% in group A and 92.2% pts in
Group B (p=0.158), disease specific OS was 100% in Group A and 96.1% in Group B
(p=0.319). On multivariate
analysis, ISUP score ≥4 was associated with worse biochemical failure (HR=2.29,
95% CI: 1.25-4.23; p=0.008); ISUP score≥4 (HR=2.08, 95% CI: 1.05-4.10, p=0.036)
and time to BCR<24 months (HR=2.24, 95% CI: 1.09-4.62, p=0.028) were significantly
associated with worse distant failure. Among pts undergoing concomitant ADT, pts
in Group A reported a lower rate of biochemical (HR=0.19; 95% CI: 0.07-0.52)
and distant failure (HR=0.17; 95% CI: 0.06-0.49) than Group B (Fig 1). A
significantly higher late genitourinary toxicity rate was observed in Group A
(p=0.032).
Conclusion
Although
the study was limited by the retrospective design, the
relative shortness of the median follow-up and the small number of pts in some
of the evaluated subgroups, our analysis did not show any significant
difference in outcome between the 2 treatment schedules except for a greater late
genitourinary toxicity in the higher BED group. Our finding of improved
biochemical and distant disease control with a higher BED hypofractionation and
concomitant ADT indicates the need to improve the selection of pts who may
benefit from integrated and intensificated SRT.