Dosimetric analysis with or without Deep Inspiration Breath-Hold in the left sided breast cancers
sanjay hunugundmath,
India
PO-1194
Abstract
Dosimetric analysis with or without Deep Inspiration Breath-Hold in the left sided breast cancers
Authors: sanjay hunugundmath1
1Sahyadri superspecialty hospital , Radiation Oncology, pune, India
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
- Radiotherapy for breast cancer presents a benefit in terms of reducing local recurrence and deaths resulting from breast cancer
- As the survival improves , the long term morbidity becomes a major concern to critical strctureslike lungs and the heart .
- Late Side effects include fibrosis , telangiectasia , pigmentation of skin , lymphedema, cardiac and lung morbidity , and many reports have suggested cardiac morbidity , irresepective of any dose to the heart .
- So we evaluated the various dosimetric parameters of heart and lung with and without abc( active breath cordinator) using DiBHtechnique during tangential field breast cancer radiation.
Material and Methods
- We have treated 50 left sided breast cancer patients, who fit into our DiBH technique using ABC
- Our inclusion criteria included :
- 1.All left sided breast cancer patients who underwent BCS
- 2.PS 0-1
- 3.Age less than 60
- 4.No previous RT to breast
- 5.No h/o any cardiac or lung disease
- 6.Any patient with a comfortable breath hold for 20-25 sec
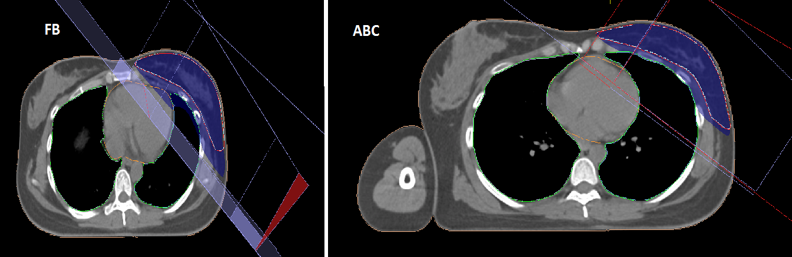
- Simulation scans of both free breathing (FB) and ABC DiBHwere done on the same patient .
- Tangent field with Field in field treatment plans with a dose prescription of 40 Gy/15frwere generated for each patient, in both the scans. UnPaired t test was the statistical test used to analyse the data and the level of significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results
- The median age group was 48 yrs. The mean threshold for breathhold was 1.2Lit .The mean duration of breathhold was 22 sec.The D mean of the heart in the FB technique was 431cGy and in the DIBH technique it was 245cGy, statistically significant with a p value of of <0.001. V30, in FB was 19 % and in DIBH group was 4% , with a p value of <0.001. The mean dose to LAD in FB was 350cGy and in DIBH it was 225cGy , reduced by 125cGy with a significant p value of 0.019
- The mean total lung volume in FB was 2411cc , and in DIBH group was 3636cc, with a significant p value of 0.001Similarly ipsilateral lung volume was 1624cc in DIBH arm and 1024cc in FB arm, with a p value of 0.001 . Mean lung dose ( D mean) of the total lung also reduced by 100cGy , but was not statistically significant
- Another interesting parameter we analysedwas breath hold volume in litre .Correlation of breathhold with various dosimetric parameters using spearmans correlation coefficient was analysed.D mean of the heart , total lung volume and ipsilateral lung volume was found statistically significant with p values of 0.002, 0.007, 0.006 respectively
PARAMETERS | FB | DIBH | P value |
D MEAN - HEART | 431cGy | 235cGy | 0.001 |
V 30 | 19%( MEAN ) | 4%( MEAN) | 0.001 |
LAD | 350cGy (MEAN) | 225cGy (MEAN) | 0.019 |
Conclusion
- We can conclude that DIBH with ABC technique has a significant impact on LAD and heart doses.
- This should be the standard of care of RT for all left sided breast caners, for the amount of benefit it gives in preventing long term cardiac morbidity.