Tangential VMAT and IMRT for WBI compared using automated multi-criterial treatment planning
PD-0749
Abstract
Tangential VMAT and IMRT for WBI compared using automated multi-criterial treatment planning
Authors: laura redapi1, linda rossi2, livia marrazzo3, joan J.Penninkhof4, stefania pallotta5, ben Heijmen6
1 University of Florence, Department of Experimental and Clinical Biomedical Sciences “Mario Serio”, Florence, Italy; 2 Erasmus MC Cancer Institute, Department of Radiation Oncology, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 3 University of Florence, Department of Experimental and Clinical Biomedical Sciences “Mario Serio”,, Florence, Italy; 4 Erasmus MC Cancer Institute, Department of Radiation Oncology, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 5University of Florence, Department of Experimental and Clinical Biomedical Sciences “Mario Serio”, Florence, Italy; 6 Erasmus MC Cancer Institute, Department of Radiation Oncology,, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
A limitation of all published studies comparing VMAT and IMRT for whole-breast
irradiation (WBI) is the use of manual planning, making results dependent on
planner experience and allotted planning time. Moreover, sample sizes are
always small, probably related to the manual planning workload. Comparisons for
deep-inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) treatment were only performed in two small
studies using manual planning and presenting diverging conclusions. The aim of
this study was to use automated planning to systematically compare for a large
cohort of left-sided breast cancer patients treated with DIBH two delivery techniques
for WBI: 1) IMRT with two tangential fields, 2) VMAT with two small tangential
arcs.
Material and Methods
Forty-eight randomly selected left-sided breast
cancer patients, treated with postoperative WBI in DIBH and daily CBCT setup
correction, were included. Patients were clinically treated with a hybrid
technique (tangential open and IMRT fields). Generation
of autoIMRT and autoVMAT plans was performed with an in-house
system for automated multi-criterial generation of deliverable IMRT and VMAT
plans, which was configured for plan generation in line with clinical
requirements. AutoIMRT and autoVMAT plans were compared in terms
of dosimetric plan parameters, estimated excess relative risks (ERR) for
toxicities, and delivery times, MUs, and delivery accuracy at a linac, the
latter assessed with an Octavius phantom with a 2D-array729 (PTW Freiburg GmbH).
Results
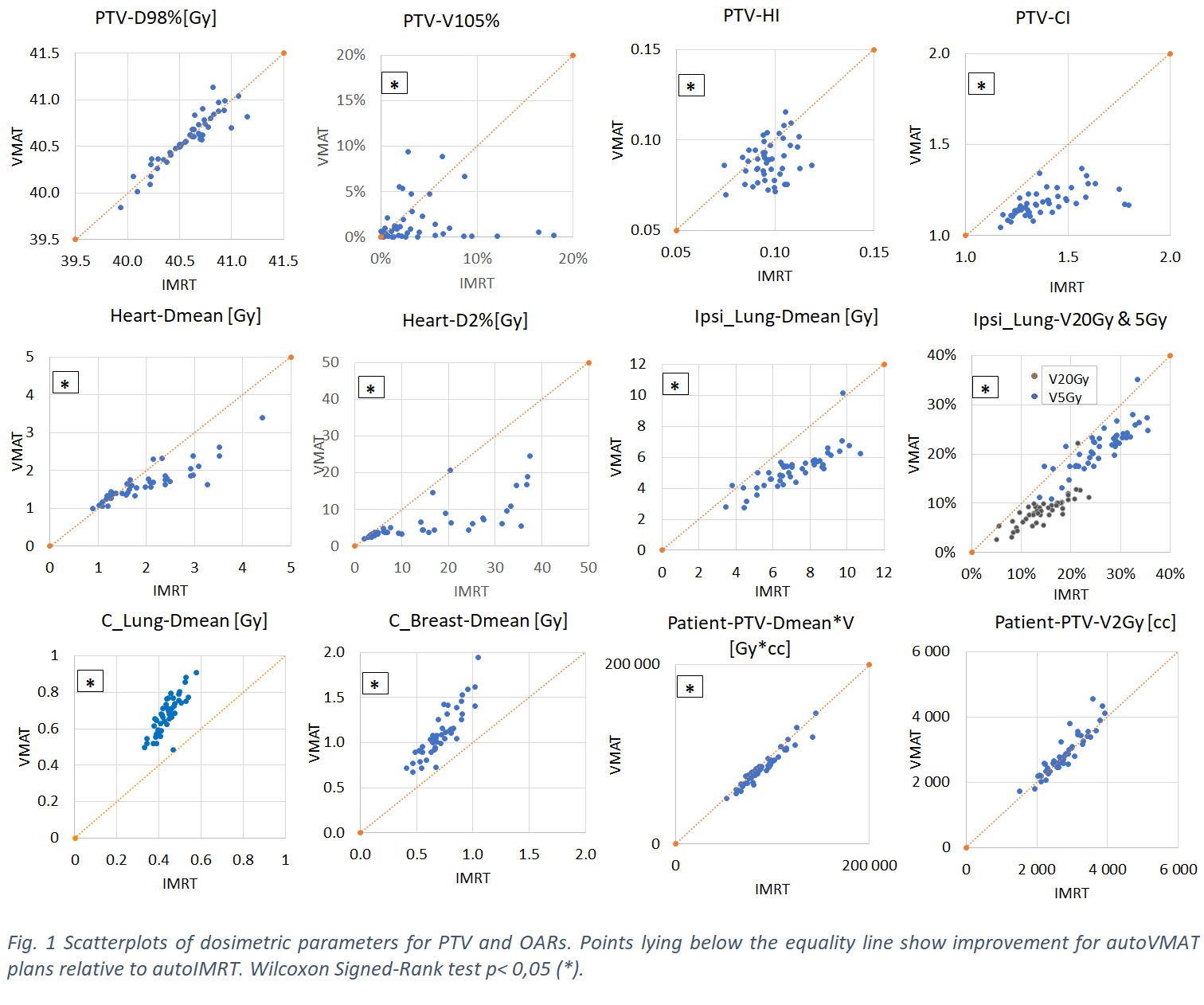
Fig. 1 shows for most patients relatively large gains for autoVMAT compared to autoIMRT in
PTV hot spots, heart and ipsilateral lung at the price of minor losses in
contralateral breast and lung. Compared to autoIMRT,
mean heart doses and mean ipsilateral lung doses in autoVMAT plans were on average reduced by 0.4 Gy (range: -0.2-1.6
Gy) and 2.0 Gy (range: -0.4-4.5
Gy), respectively with estimated average
ERR reductions for major coronary events and ipsilateral lung tumors of 3%
(range: -1%-12%)
and 17% (range: -3%-38%),
respectively. There were no statistically significant differences in ɤ passing
rates, while a moderate increase in treatment time (68 vs 52 s) and an
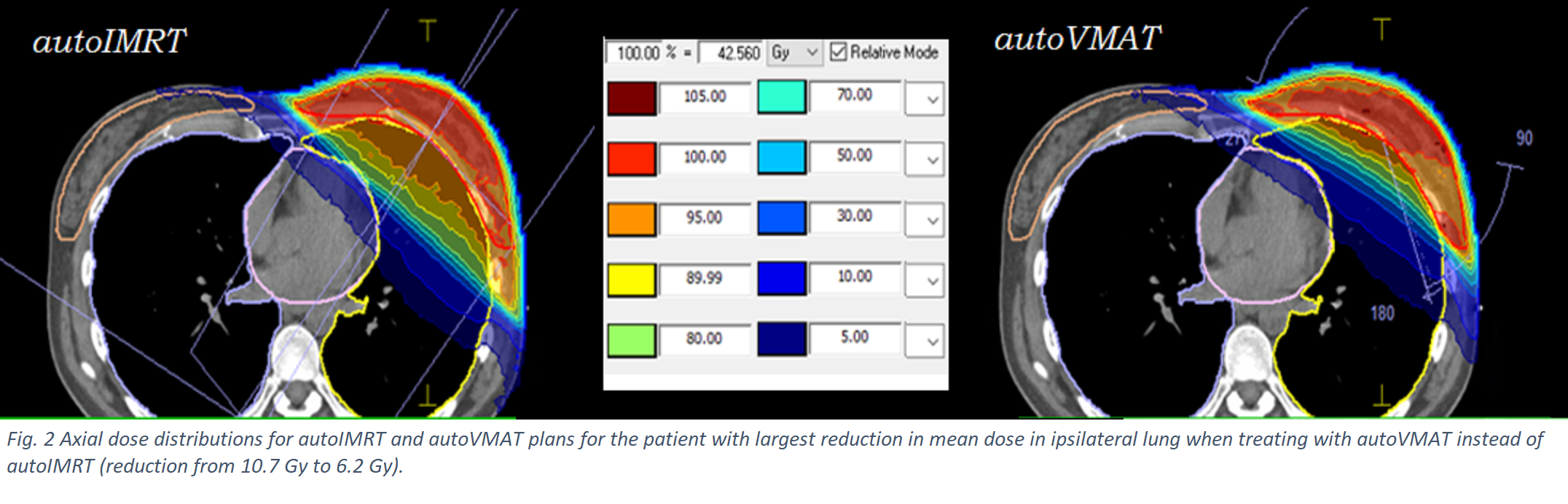
improvement in MUs (675 vs 273) for autoVMAT were observed. Fig. 2 presents
for a selected patient autoVMAT and autoIMRT dose distributions, showing
reduced ipsilateral lung and heart doses with autoVMAT and slightly
enhanced contralateral breast dose.
Conclusion
For left-sided WBI in DIBH, autoVMAT with two tangential subarcs was overall favourable compared to autoIMRT
with two tangential static fields.
Although autoVMAT was favourable for most patients, for some
patients, autoIMRT could have been a better choice because of
a significantly lower contralateral breast dose. Automatic generation of an autoIMRT and an autoVMAT plan for each patient could be used for personalized
selection of the best patient-specific plan, without
increasing planning workload.