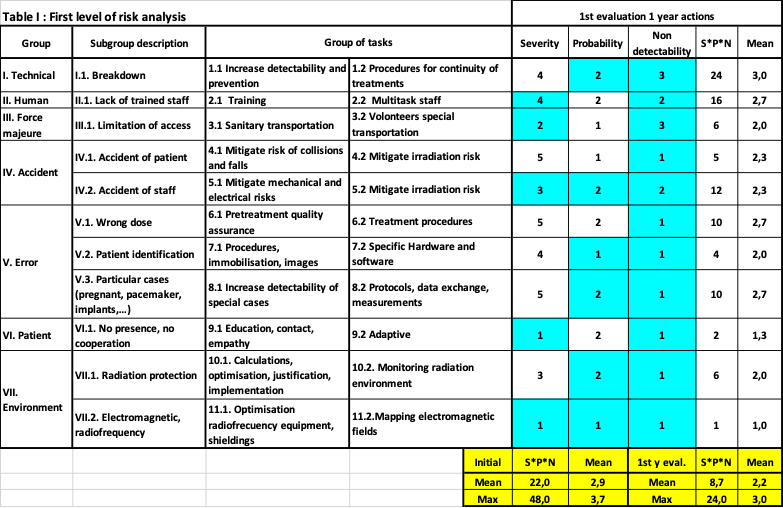
Seven groups and 11 subgroups of risks where listed, from technical to environment. We assigned 2 groups of tasks to eliminate or mitigate each risk. A grid from low (1) to severe (5) evaluate the severity (S), the probability (P) and the non-detectability (N). The S*P*N initial figure of merit had a maximum of 48 and a mean of 22.
Table I shows a mitigation of the S*P*N factor to a maximum of 24 and a mean of 8,7 after performing 77% of tasks (31 for this table) assigned to small groups. Evaluations were performed systematically and before critical milestones (installation, acceptance-commissioning, starting clinical).
A typical example of group of tasks were related to risk of breakdown and need to warranty the continuity of treatments. In a backup task, a 7-level root decision approach included night and Saturday shifts, a circuit of photon backups with pre-calculations and common immobilisations.
The quality of the dose, clinical procedures, treatments and the full process was warrantied with external audits, protocols, intercomparisons (IROC-USA, NPL-UK, Centre Antoine Lacassage-Nice-France, ISOP, ISO9001,…), and for the individual cases through comparisons photons-protons, use of double energy CT for implants, weekly adaptive, and organ movements management (Vision RT and DynR spirometer). A systematic collection, analysis and action of precursors and undesirable events is performed.