Validating Brain Metastases Velocity for survival prediction in patients treated with radiosurgery
Michael Mayinger,
Switzerland
PD-0734
Abstract
Validating Brain Metastases Velocity for survival prediction in patients treated with radiosurgery
Authors: Michael Mayinger1, Kim Borsky1, Johannes Kraft1, Simon Frei1, Luisa Sabrina Stark1, Janita van Timmeren1, Stephanie Tanadini-Lang1, Matthias Guckenberger1, Nicolaus Andratschke1
1University Hospital Zurich, Radiation Oncology, Zurich, Switzerland
Show Affiliations
Hide Affiliations
Purpose or Objective
Brain Metastases Velocity (BMV) is a recently
developed prognostic tool taking brain metastases occurrence dynamics into
account. So far, there are three different BMV scores considering the velocity
of first occurrence of brain metastases (initial BMV; iBMV) or the recurrence
of brain metastases after brain-directed therapy (classical BMV; cBMV and
volumetric BMV; vBMC). The aim of our study was to validate all three scores in
a patient cohort treated for brain metastases with stereotactic radiotherapy.
Material and Methods
We retrospectively evaluated medical records of 386
patients with BM disease receiving stereotactic radiation therapy between
January 2014 and December 2019. iBMV, cBMV, and vBMV were calculated.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to compare overall survival (OS).
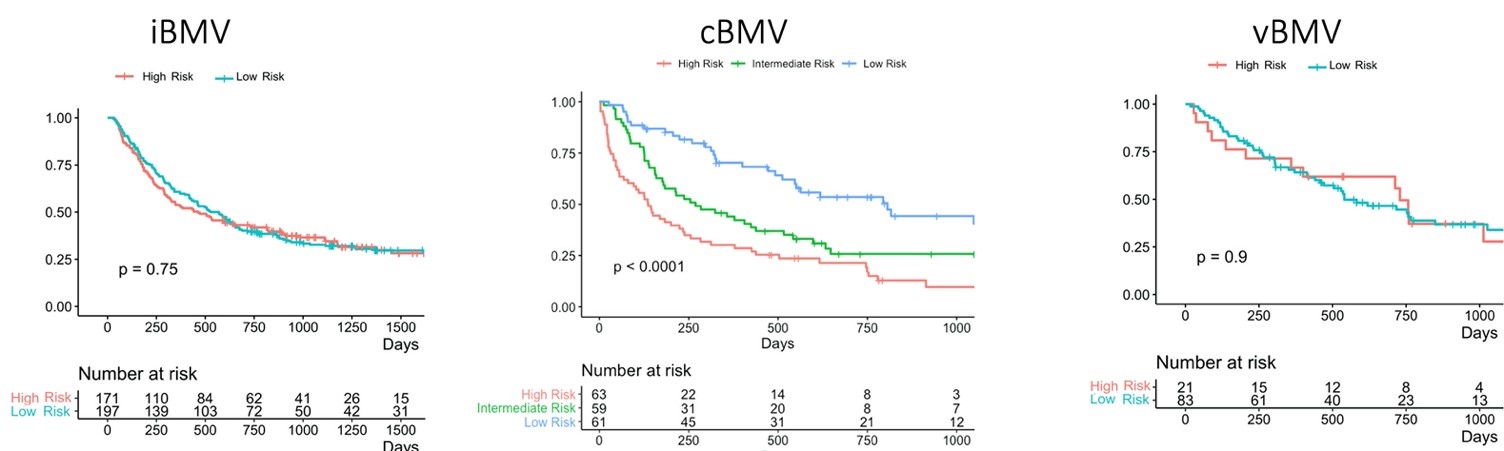
Results
After a median follow‐up of 14 months (interquartile
range: 5 –31), 1 year survival rate was 53%. 183 patients received a
minimum of two treatments and 33 at least three treatments (range: 1-7
courses). The iBMV (including all 386 patients; p = 0.75) and the vBMV (104
patients where brain metastases volume was available; p = 0.9) could not
sufficiently stratify the patients into different risk groups. The cBMV
determined for 183 patients with distant brain failure, was able to
significantly separate the different risk groups regarding OS (p <
0.001). At baseline, univariate analysis revealed the extracranial metastatic
disease status and GPA to be significant predictors for OS. At first distant
brain failure (DBF) extracranial metastatic disease status, karnofsky
performance status, GPA and RPA represented prognostic factors.
Conclusion
In this BM cohort treated homogeneously with
stereotactic radiotherapy, only cBMV was able to separate the different risk
groups. In general, cBMV may be a valuable tool to decide on salvage radiosurgery
for patients with DBF.