The two checklists were first examined for
applicability in AI-based algorithms. Some of the items for each guideline
required adaptations to suit evaluation of the AI models (e.g. missing data was
replaced with suboptimal plans).
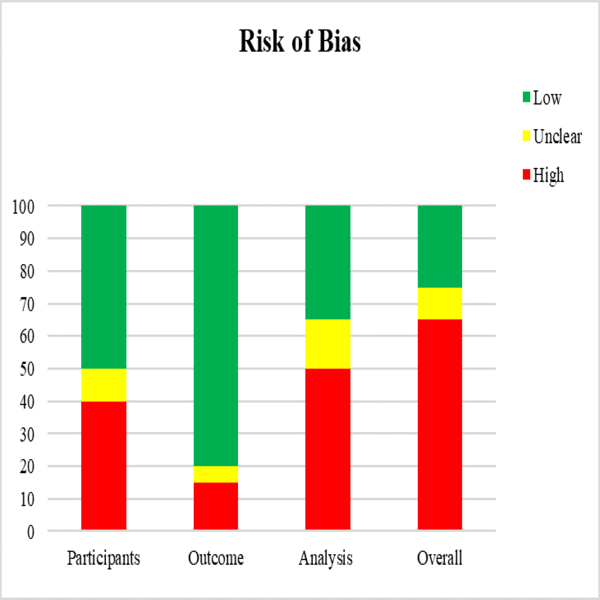
Figure 1. PROBAST risk of
bias assessment
Figure 1 reports the ROB assessed using the tailored PROBAST items for
the 20 analysed articles.
Analysis domain is the major
cause of ROB in AI-based treatment planning studies (50% of the studies). In
these studies, the steps on how to deal with suboptimal plans is either
under-reported or unclear.
Adherence to the tailored
TRIPOD items was poor in blinding (15%), sample size (10%), and suboptimal plan
reporting (15%). Furthermore, given the statistical complexity of model development/validation,
the statistical methods used are neglected, resulting in a high ROB. Only 20%
of the studies provided supplementary material such as a full model description or code, the statistical analysis or the
study data sets (Figure 2).
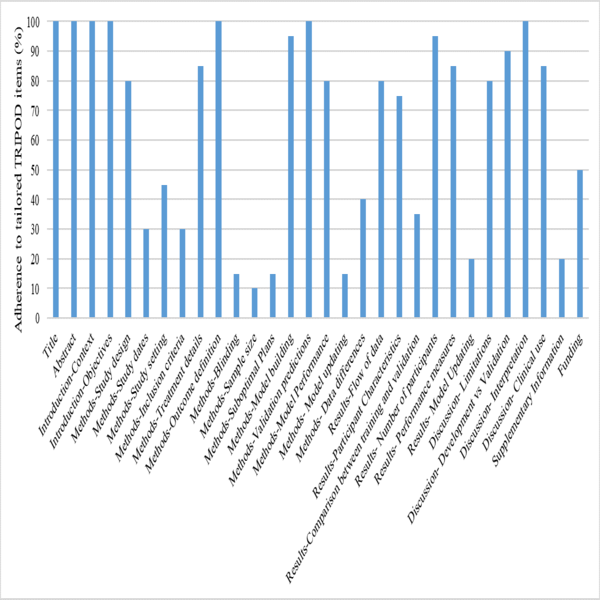
Figure 2.Adherence to
individual TRIPOD items