IC50 was 0,9654
nM; 0,6836 nM;1,296 nM;0,8549 nM for RS,LPS,LMS and FS respectively. Significant
reduction of SF in LMS and LPS cell lines was observed following
IR+trabectedin as compared to IR alone, resulting in ER50 of 2.35 and 1.45,
respectively. (Fig.A)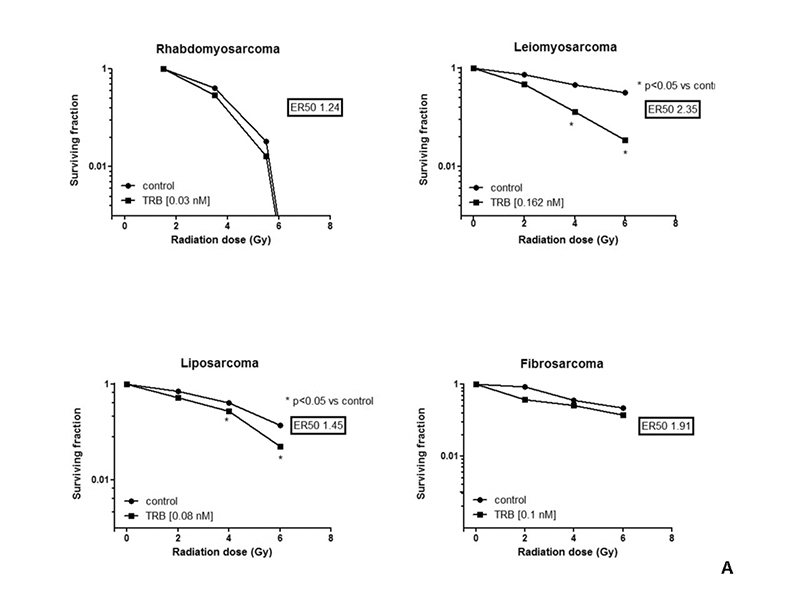
All STS cell
lines showed a significantly reduced invasiness following trabectedin alone or trabectedin+IR
compared to control and trabectedin+IR compared to IR alone. Trabectedin+IR
compared to control, resulted in an increasing, similar or reduced G2/M phase
cell fraction of cells in LPS, FS and RS/LMS, respectively. In all STS cell
lines, trabectedine+IR induced a significantly higher occurrence of γ-H2AX foci
compared to control, trabectedin and IR alone. Reduction in the fluorescence
intensity associated to the number of foci over 24 hour was significantly lower
in the combined treatment arm.